The internet of things: an overview
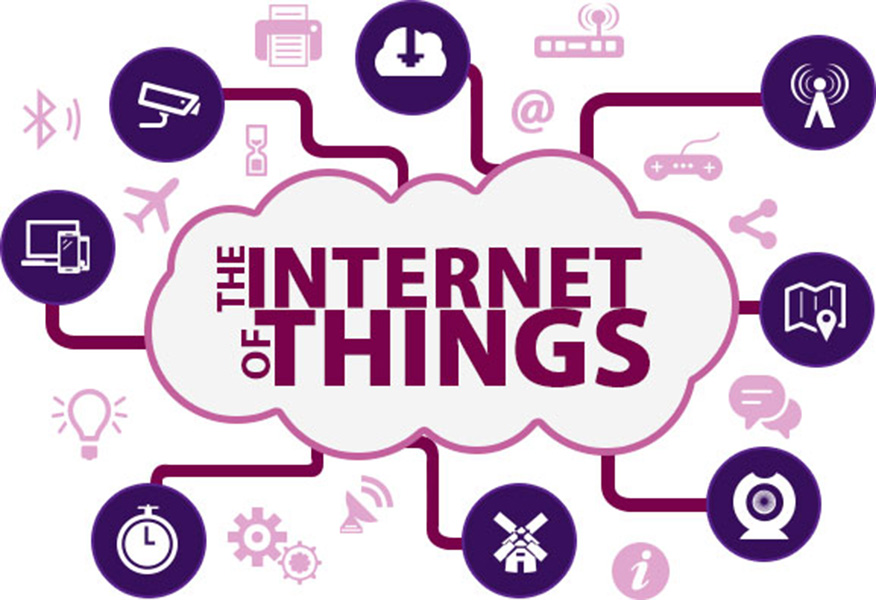
The internet of things (IoT) is a computing concept that describes a scenario where everyday physical objects are internet of things iotconnected to the internet and can identify themselves to other devices or processes, via an IP address.The IoT is significant because an object that can represent itself digitally becomes something greater than the object by itself. No longer does the object just relate to the process; it now connects to surrounding objects and database data, permitting “big data” analytics and insights. In particular, “things” might communicate autonomously with other things and other devices, such as sensors in manufacturing environments or an activity tracker with a smartphone.
IoT has evolved from the convergence of wireless technologies, micro-electromechanical systems, microservices and the internet.This convergence has torn down the walls between operational technology and information technology, allowing unstructured machine-generated data to be analysed for insights that will drive improvements and cost reduction.Consumer IoT took another revolutionary path, either by becoming connected – for example, speed sensors on a bike – or being newly invented. In other instances, such as in healthcare, things have been there but not widely used, such as patient health status.
IoT: countless use cases
There are countless use cases where IoT can be deployed, such as in manufacturing, vehicles and even future cases such as smart cities and energy.
internet of things dreamsterManufacturing, as an example, has been operating shop floor equipment for decades with sensors that control machine processes, but these sensors have been relatively dumb, have not been IP enabled nor have they been able to communicate beyond their local process. This situation is changing; manufacturing equipment is now being produced with sensors that are IP-enabled, can communicate with each other, collect and disseminate data in real-time. There are many benefits to the manufacturer such as: control of product rotation, automate restocking processes, production line monitoring, quality assurance real-time alerts etc.
A smart city is defined as a city that monitors and integrates conditions of its entire critical infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, tunnels, rail, airports, seaports, water, power and major buildings. With the use of IoT technology, the city planners can better optimise their resources, plan preventive maintenance, monitor security and control emergency response, through advanced monitoring systems and built-in smart sensors with data collected and evaluated in real-time.
IoT can play a role in health care with smart devices used for many cases. The elderly or disabled could live independently with fall detection devices and/or physical activity monitoring through body sensors; patient surveillance sensors for hospitals or care homes, smart sensors to control conditions in medical storage units and devices to monitor ultraviolet radiation on people.